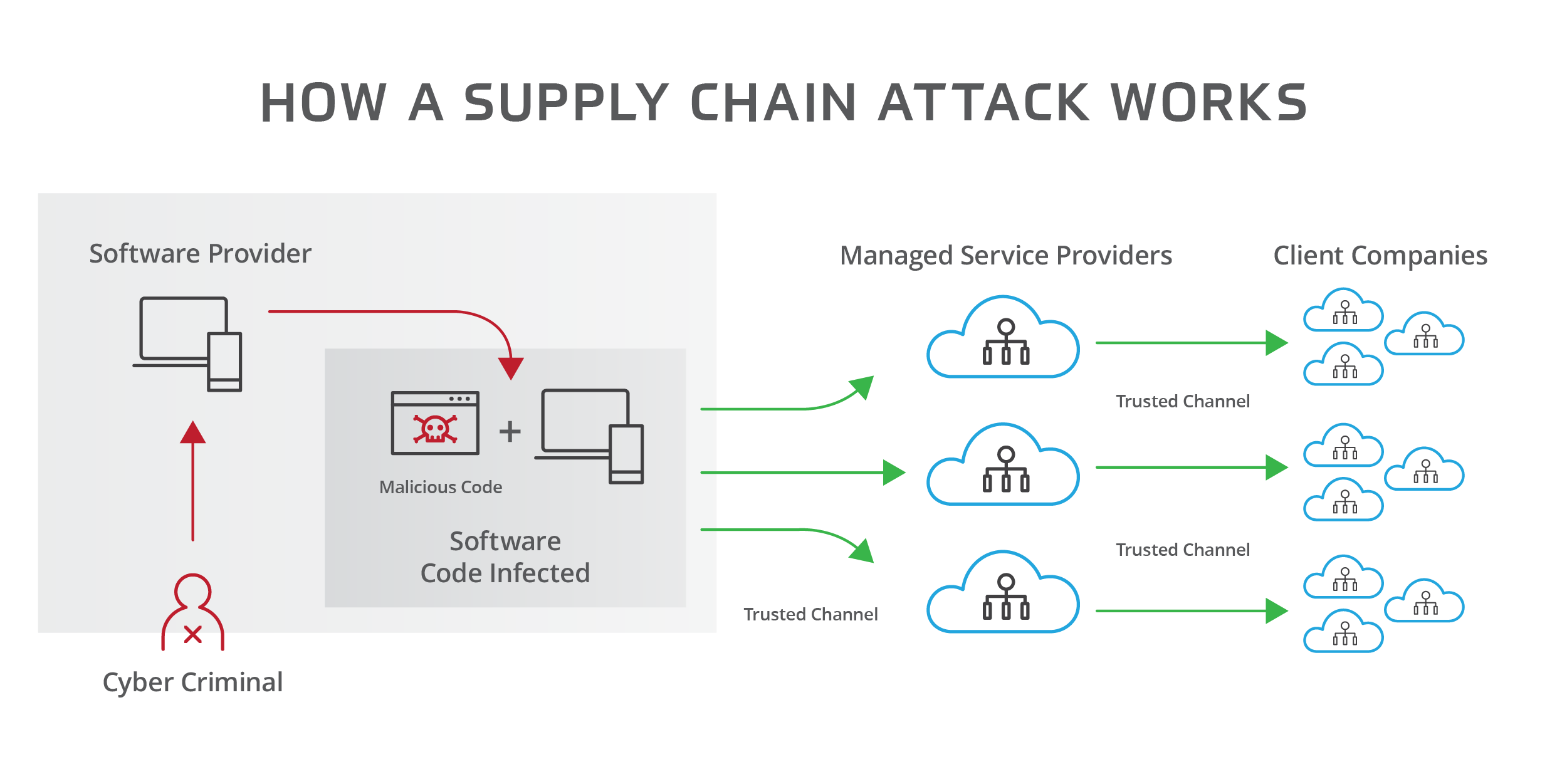
Supply Chain Cyber Attacks
Supply chain cyber attacks are growing threats in today’s world. These attacks target the weak links in a company’s supply chain. A supply chain involves all the steps taken to deliver a product or service, from its creation to the customer’s hands. In a cyber attack on a supply chain, hackers find a vulnerable point, such as a smaller partner or third-party vendor. They then use this to breach the security of the entire system.
The goal of these attacks is to cause harm to a business, disrupt operations, or steal sensitive information. The danger lies in the fact that supply chains often include many different parties. A breach in just one link can expose an entire network of companies. This makes supply chain cyber attacks particularly harmful because they can spread quickly, affecting multiple organizations at once.
Many times, large companies are the main targets, but smaller suppliers are often the gateway for these attacks. Hackers know that smaller companies may not have the same level of security as larger ones, making them easier to penetrate. Once they infiltrate a supplier’s system, they gain access to the larger organization that works with them.
Some common techniques used in these attacks include phishing (tricking people into giving out sensitive information), malware (harmful software), and ransomware (holding data hostage for payment). As these attacks increase, it’s essential for companies to stay alert and secure their entire supply chain, not just their own operations.
Recent News on Supply Chain Cyber Attacks
In recent years, supply chain cyber attacks have made headlines worldwide. A notable example is the SolarWinds attack in 2020. SolarWinds, a software company, unknowingly became the source of a major cyber attack. Hackers inserted malicious code into their software update, affecting thousands of their customers, including government agencies and large corporations. This attack was one of the biggest and most damaging in history because it went unnoticed for months, giving hackers plenty of time to access sensitive information.
Another significant event was the Kaseya attack in 2021. Kaseya, a company that provides IT management software, was targeted in a ransomware attack. Hackers used Kaseya’s software to spread ransomware to its customers, including managed service providers (MSPs) who serve many small and medium-sized businesses. The attack caused widespread disruptions, and businesses in multiple countries were affected.
These incidents highlight how hackers are shifting their focus to supply chains as a way to cause maximum damage. By targeting widely used software or services, attackers can affect a broad range of organizations at once. The consequences are not just financial but can also include loss of trust, damaged reputations, and national security risks.
Governments around the world have recognized the seriousness of supply chain cyber attacks. In response, new regulations and laws have been introduced to strengthen the security of supply chains, particularly in critical sectors like healthcare, energy, and finance. These measures aim to ensure that companies are better prepared to prevent and respond to these types of threats.
How Companies Can Protect Against Supply Chain Cyber Attacks
Protecting against supply chain cyber attacks requires a proactive approach. Companies must not only focus on securing their own systems but also ensure that their suppliers and partners are following strict security protocols. Here are some key strategies that can help companies strengthen their defenses.
First, it is important to perform regular risk assessments. By identifying potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain, companies can take steps to address them before they are exploited. This includes evaluating the security practices of third-party vendors and suppliers. Many companies now require their partners to meet specific cybersecurity standards before working with them.
Second, companies should invest in advanced security technologies. Tools like firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication can make it harder for hackers to break into systems. In addition, using artificial intelligence (AI) to detect unusual behavior in networks can help identify potential threats before they cause harm.
Third, it is essential to create a culture of cybersecurity within the organization. Employees should be trained regularly on how to spot phishing attempts, avoid malware, and report suspicious activities. Many cyber attacks start with human error, so educating employees is one of the best defenses.
Lastly, companies should have an incident response plan in place. This plan outlines the steps to take if a breach occurs, including how to contain the threat, communicate with stakeholders, and recover from the attack. The quicker a company can respond, the less damage will be done.
Collaboration is also key. Companies should work closely with their suppliers, partners, and even competitors to share information about potential threats and best practices. Industry-wide efforts to improve supply chain security can help reduce the overall risk of attacks.
Analysis of the Impact of Supply Chain Cyber Attacks
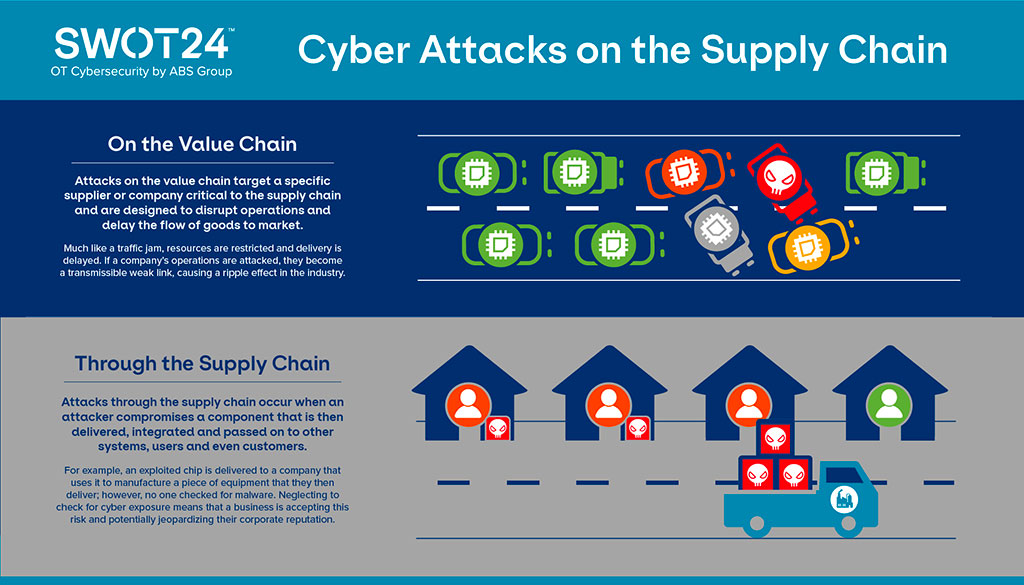
The impact of supply chain cyber attacks can be devastating. One of the most immediate consequences is financial loss. Companies may lose millions of dollars due to downtime, ransom payments, or the cost of repairing systems. Additionally, businesses can face fines if they fail to comply with cybersecurity regulations. For smaller companies, a major cyber attack could even lead to bankruptcy.
Beyond financial damage, supply chain cyber attacks can have long-lasting effects on a company’s reputation. When customers and partners lose trust in a company’s ability to protect their data, they may take their business elsewhere. This loss of trust can take years to rebuild, and in some cases, a company may never fully recover.
The disruption caused by these attacks can also be widespread. A single breach in a supply chain can cause delays in production, shortages of goods, and even affect entire industries. For example, the Colonial Pipeline attack in 2021, though not a supply chain attack in the traditional sense, demonstrated how a cyber attack on a critical infrastructure company can cause fuel shortages and widespread panic.
In some cases, the impact goes beyond business and affects national security. Governments are increasingly concerned about the potential for cyber attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and healthcare systems. A successful attack on these sectors could disrupt essential services and put lives at risk.
It is clear that supply chain cyber attacks are not just an IT problem; they are a business and national security issue. Companies must take these threats seriously and invest in strong cybersecurity measures to protect their operations and the broader economy.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Cybersecurity
As technology continues to evolve, so do the tactics used by cybercriminals. Experts predict that supply chain cyber attacks will become more frequent and more sophisticated in the coming years. To stay ahead of these threats, companies will need to adopt new technologies and approaches.
One trend that is expected to grow is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cybersecurity. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to detect unusual patterns and identify potential threats in real time. By using AI and ML, companies can respond to attacks more quickly and effectively.
Another trend is the increasing focus on zero-trust security models. In a zero-trust approach, every user, device, and application is treated as a potential threat, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network. This approach requires strict verification for anyone trying to access sensitive systems, reducing the chances of a breach.
Collaboration between governments and private companies is also expected to play a key role in future cybersecurity efforts. As the threat of supply chain cyber attacks grows, governments are likely to introduce more regulations and guidelines to ensure that companies are taking the necessary steps to protect their supply chains.
Additionally, blockchain technology is being explored as a potential solution for securing supply chains. Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it harder for hackers to manipulate data, and its transparency can help companies track and verify the security of their supply chains.
The future of supply chain cybersecurity will be shaped by both new technologies and the lessons learned from past attacks. By staying informed and investing in strong defenses, companies can reduce their risk and protect themselves from the growing threat of supply chain cyber attacks.