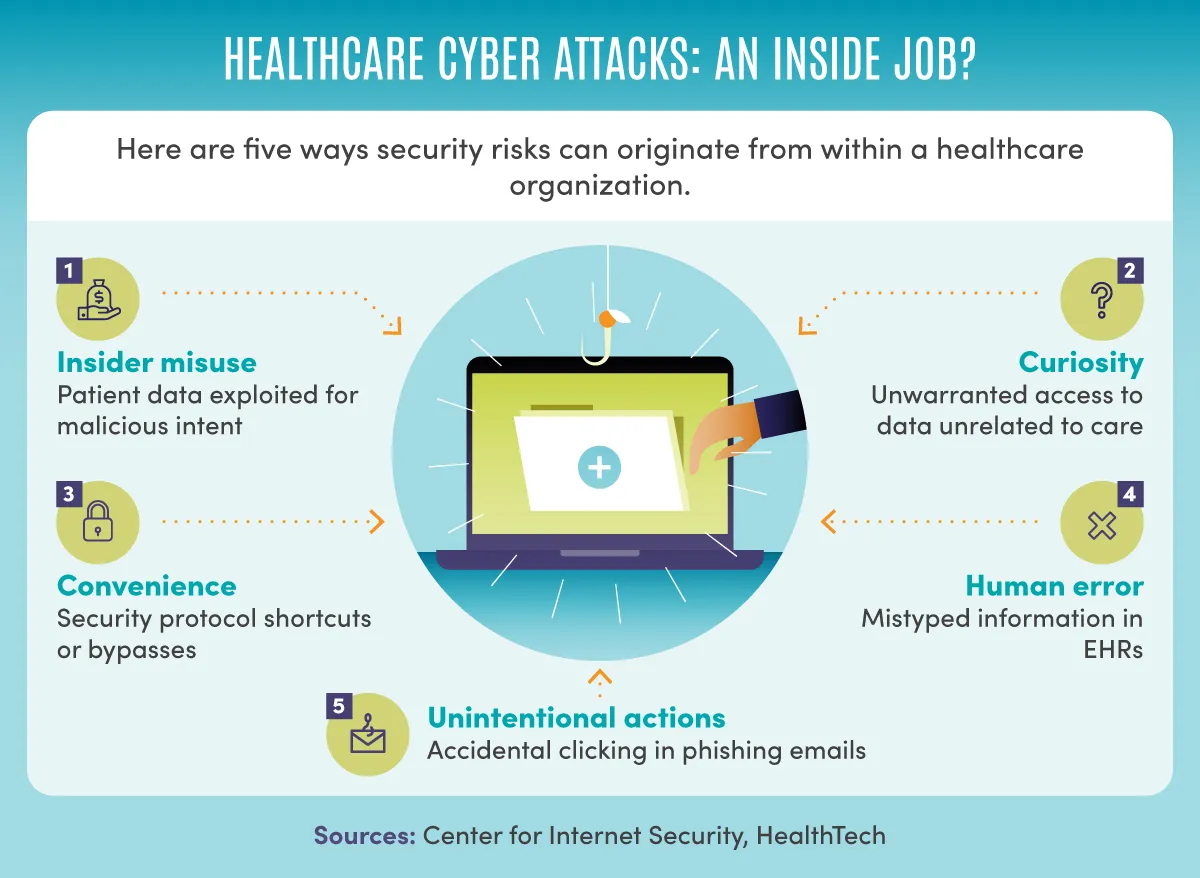
Cyber Fraud: What Is It?
Cyber fraud involves dishonest activities conducted through the internet or other digital platforms to gain something of value. This value could be money, personal information, or access to sensitive data. Cyber fraud includes various scams and deceptive practices designed to trick individuals or organizations into giving up their assets or confidential information.
Cyber fraud can take many forms, such as phishing scams, where fraudsters pose as legitimate organizations to steal personal information; ransomware attacks, which lock users out of their systems until a ransom is paid; and identity theft, where criminals steal and misuse someone’s personal details.
The rise of cyber fraud is linked to the increasing reliance on digital technologies in everyday life. With more people conducting financial transactions and sharing personal information online, the opportunities for fraudsters to exploit vulnerabilities have grown. Understanding the different types of cyber fraud can help individuals and organizations take preventive measures to protect themselves.
Recent Cases of Cyber Fraud
1. The Capital One Data Breach
One of the most notable recent cases of cyber fraud is the Capital One data breach. In 2019, a former employee of Amazon Web Services exploited a vulnerability in Capital One’s systems to access the personal information of over 100 million customers. The breach exposed sensitive data, including names, addresses, credit scores, and even some bank account numbers. The perpetrator was arrested and charged, but the incident highlighted significant issues in data security practices and the importance of securing cloud-based systems.
2. The SolarWinds Hack
Another major cyber fraud case is the SolarWinds hack, which came to light in late 2020. Hackers, believed to be affiliated with a foreign government, compromised SolarWinds’ software updates to infiltrate numerous U.S. government agencies and private companies. The attack, which was sophisticated and covert, allowed the hackers to spy on and gather information from targeted organizations. This incident emphasized the growing threat of cyber espionage and the need for improved security measures in software development and IT infrastructure.
3. The Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack
In May 2021, Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel pipeline operator in the U.S., suffered a ransomware attack that disrupted fuel supplies across the Eastern United States. The attackers, identified as a criminal group known as DarkSide, encrypted Colonial Pipeline’s data and demanded a ransom payment. The company initially paid the ransom but later managed to recover much of the stolen data. This attack demonstrated the severe impact of ransomware on critical infrastructure and the challenges of responding to such threats.
Current Trends in Cyber Fraud
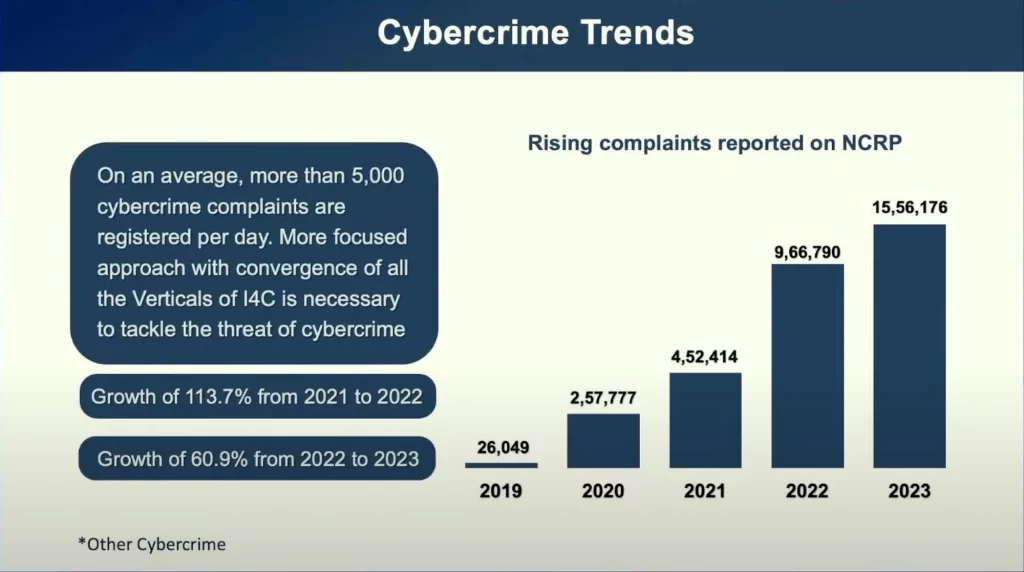
1. Increased Sophistication of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated. Cybercriminals are using more convincing methods to trick individuals into revealing personal information. For example, phishing emails might appear to come from trusted sources like banks or social media platforms, and they may include realistic-looking websites designed to steal login credentials. The rise of phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platforms has also made it easier for less experienced attackers to launch sophisticated phishing campaigns.
2. Ransomware Evolution
Ransomware attacks continue to evolve, with criminals adopting new techniques and targeting a wider range of victims. Modern ransomware attacks often involve double extortion tactics, where attackers not only encrypt data but also threaten to release sensitive information if the ransom is not paid. Additionally, ransomware groups are increasingly targeting high-profile organizations and critical infrastructure, aiming for larger payouts and more significant disruptions.
3. Rise of Deepfakes
Deepfakes, which use artificial intelligence to create realistic but fake audio and video content, are emerging as a new tool for cyber fraud. Fraudsters can use deepfake technology to impersonate individuals in video or voice recordings, potentially tricking victims into making financial transactions or revealing confidential information. The ability to create convincing deepfakes poses a serious challenge for verifying the authenticity of digital content and detecting fraud.
How to Protect Yourself from Cyber Fraud
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
One of the simplest and most effective ways to protect yourself from cyber fraud is to use strong, unique passwords for different accounts. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common words. Instead, create passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts. Even if a fraudster obtains your password, they will still need a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or an authentication app, to access your account. Enabling 2FA can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts.
3. Be Cautious with Emails and Links
Always be cautious when opening emails or clicking on links, especially if the email is from an unknown sender or seems suspicious. Verify the sender’s email address and look for signs of phishing, such as grammatical errors or urgent requests for personal information. If you receive an email asking you to click on a link or download an attachment, verify its legitimacy before taking any action.
Keep Your Software Up-to-Date
Regularly updating your software, including your operating system, applications, and antivirus programs, helps protect your devices from the latest security vulnerabilities. Software updates often include patches for known security issues, so keeping your software current is crucial for safeguarding against cyber threats.
Educate Yourself and Others
Stay informed about the latest trends and threats in cyber fraud. Education and awareness are key to preventing and responding to cyber fraud. Share information about cybersecurity best practices with friends, family, and colleagues to help create a safer online environment for everyone.
This blog provides an overview of cyber fraud, recent high-profile cases, current trends, and practical tips for protecting yourself from these threats. Staying informed and vigilant is crucial in today’s digital landscape to avoid falling victim to cyber fraud.